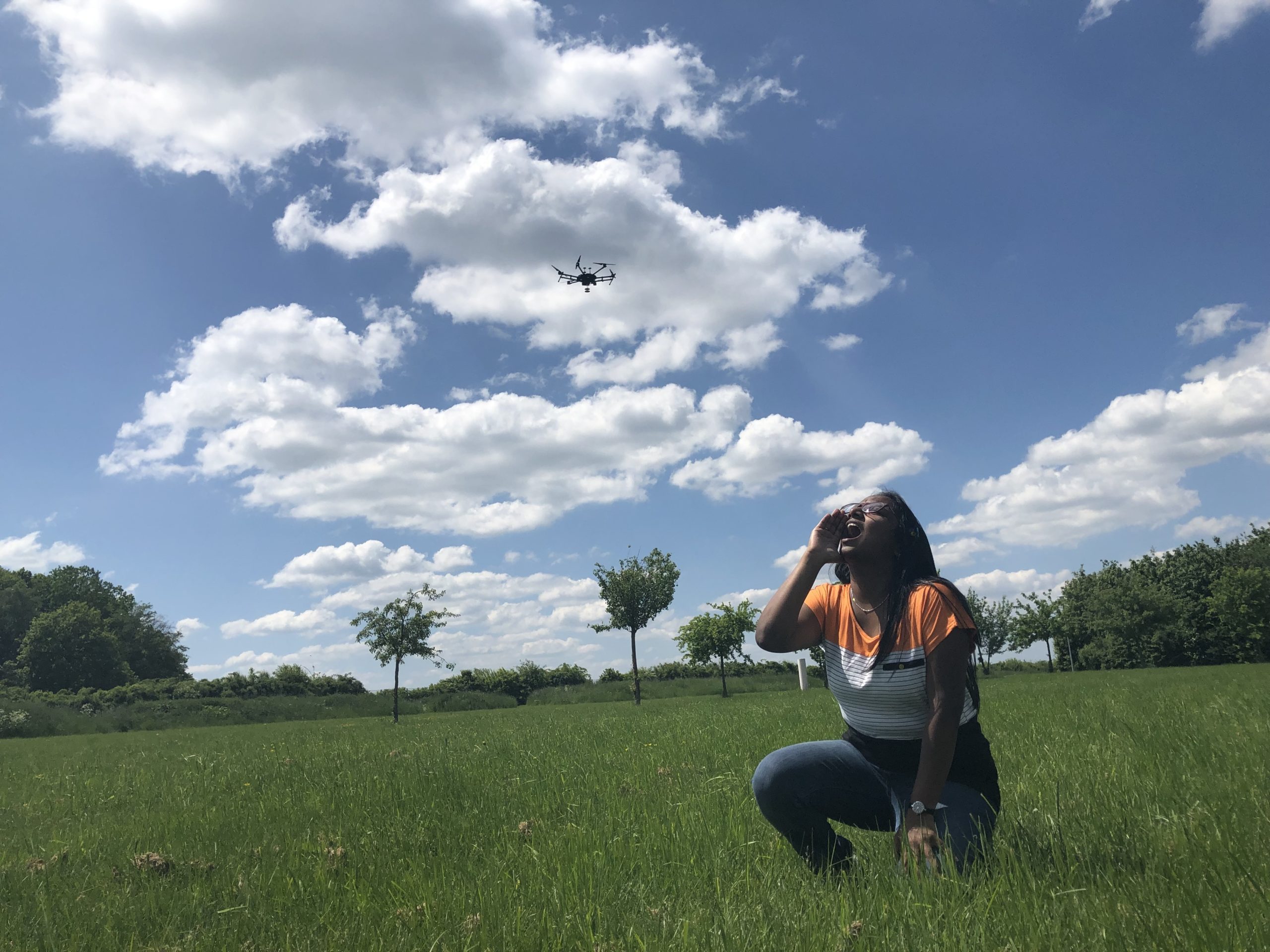
Scientists are training drones to hunt people down by following the sound of their screaming.
Yes, it does sound like the beginnings of a Terminator/Quiet Place-style dystopia, but it isn’t meant that way. Rather, these drones are intended to save lives.
Researchers from Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Communication, Information Processing and Ergonomics (Fraunhofer FKIE) are developing scream-seeking drones to help rescue workers quickly find people who are trapped or injured in emergency situations. Mounting an array of microphones onto a drone, the researchers can hone in on screams by using processing techniques such as beamforming, which enables the microphones to detect which of them is closest to a sound and then hone in on it.
Speaking to Mashable via email, researcher Macarena Varela explained that she and colleagues Wulf-Dieter Wirth and Manfred Okum previously developed a similar system in 2016, but it had been too big and heavy to mount on a drone.
“In 2018, Dr Wirth was convinced that we could use MEMS [microelectromechanical system] microphones instead of the traditional condenser microphones, making the system much smaller,” said Varela. “This was the beginning of our dream to be able to mount it on a drone for the purpose of SAR (Search and Rescue).”
The research was presented at the Acoustical Society of America’s 180th meeting in June.

Credit: Macarena Varela
The researchers’ system currently utilises 32 microphones in its array, though Varela notes they haven’t yet experimented to find the minimum number it could use while still being effective. Even so, they consider that more is better in this case.
“Since MEMS microphones are so small and affordable, we are planning to double the amount of microphones in the near future instead of reducing them,” said Varela.
Increasing the number of microphones will allow researchers to more accurately estimate the angle of sounds they detect, as well as pick up audio that is further away. This will enable the drone to determine the location of the victim with increased precision.
“Ideally, to use beamforming techniques, it is practical to use an array of identical microphones delivering synchronous data,” said Varela. “We opted for a very particular array called Crow’s Nest, where all microphones are randomly positioned in a sphere. This type of array provides sound coverage in every direction and [is] equally good in all directions.”
“The data from all microphones is combined, after adding delays or phases to it, in order to achieve the maximum sensitivity for a selected direction, and thus forming a sensitivity beam,” continued Varela. “Then, by varying or scanning the direction, the search for sound sources is achieved.”
The researchers use the monopulse radar technique to establish the exact angle of the sound. This technique compares at least two simultaneous beams received from slightly different directions, determining which signal is stronger to detect the position of a target.
Valera and her colleagues are currently developing and testing filtering methods in order to reduce noise such as the sound of the drone’s rotor. At the same time, they are also experimenting with various detection methods for picking up the sound of people in distress, including AI and neural networks. For both purposes, Fraunhofer FKIE’s researchers are using an audio database which includes “impulsive sounds…. that victims may produce, such as tapping, clapping and screaming.”
“In previous tests in the lab, we were able to detect impulsive sounds, such as clapping, having rotor noises present,” said Varela. “We are currently processing the data with the drone flying.”
Varela provided Mashable with video demonstrating their ongoing research.
Drones are already used in search and rescue efforts, capable of reaching areas that are difficult to access as well as covering a lot of ground much more quickly than humans or dogs. However, such efforts typically rely on a human monitoring a camera mounted on a drone. Locating victims of a disaster quickly is often critical to their survival, so any technology that helps first responders find them is useful.
It may be some time before we see this system in action, though. Varela says that it “depends on how many hours [she and her colleagues] can work on it.” Testing is still ongoing, and the researchers haven’t had any concrete deadlines. Still, they believe the system has significant potential.
“A big part of the work is to now transfer the methods already implemented on the big system to this smaller one,” said Varela. “Nevertheless, we also face new challenges, such as the drone noise while flying. In other words, we have the expertise in our team, so it’s a matter of time.”